1. Ultimate Guide: 5 Signs Of Earlystage Salivary Gland Cancer

Introduction to Salivary Gland Cancer

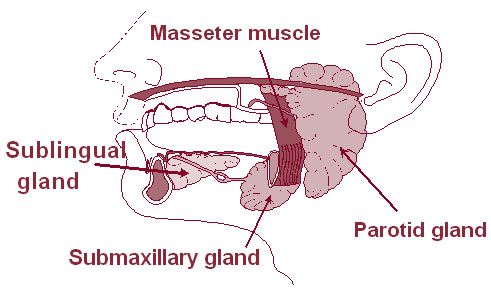
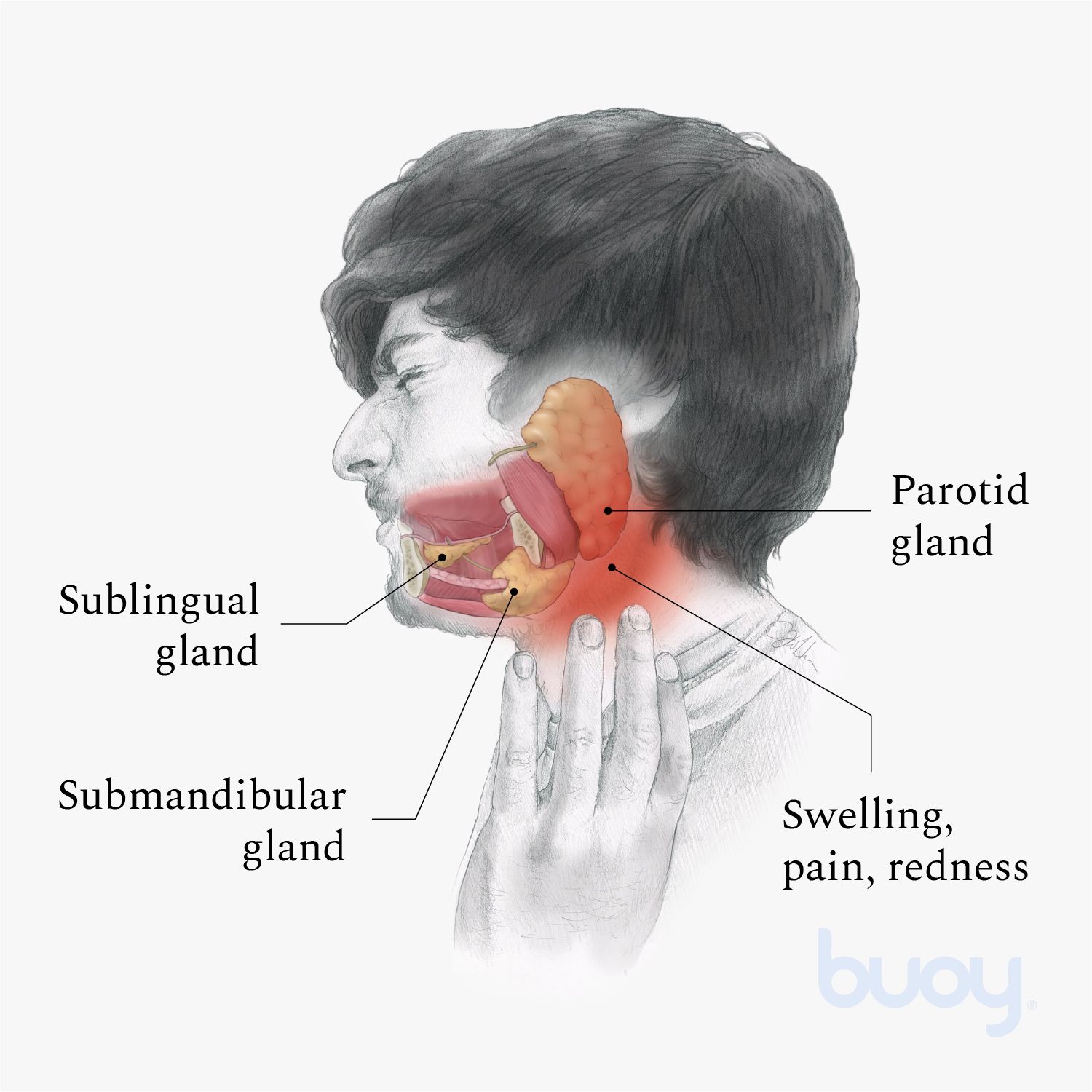
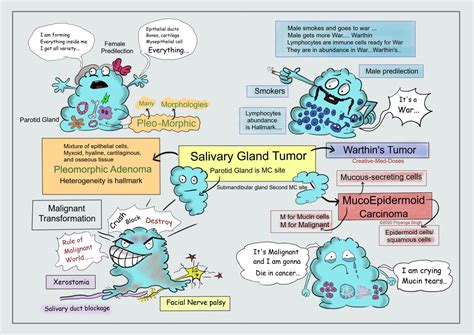
Salivary gland cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops in the glands responsible for producing saliva in your mouth. These glands include the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands, among others. While it is important to be aware of the potential signs and symptoms, it is equally crucial to remember that many of these indicators can also be associated with less serious conditions. However, early detection and prompt medical attention are key to effective management and treatment.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the early-stage signs of salivary gland cancer, helping you recognize potential red flags and seek appropriate medical advice.
Recognizing the Symptoms
1. Swelling and Lumps

One of the most common early indicators of salivary gland cancer is the presence of swelling or lumps in the areas where the salivary glands are located. This includes the sides of the neck, under the jaw, or near the ears. These swellings may be painless and can sometimes be mistaken for benign cysts or infections. However, it is important to have any persistent or growing lumps evaluated by a healthcare professional.
2. Facial Weakness or Paralysis

Salivary gland cancer can sometimes affect the facial nerves, leading to weakness or paralysis on one side of the face. This condition, known as facial nerve palsy, can cause drooping of the eyelid, mouth, or entire side of the face. It may also result in difficulty closing one eye or an asymmetrical smile. If you experience any facial muscle weakness or changes in facial expression, it is essential to consult a doctor.
3. Persistent Pain
While pain is not always a prominent symptom of salivary gland cancer, some individuals may experience persistent pain or discomfort in the mouth, jaw, or neck. This pain may be dull, aching, or sharp and can be exacerbated by certain movements or activities. If you have ongoing pain in these areas that does not respond to over-the-counter pain relievers, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation.
4. Difficulty with Swallowing and Speaking
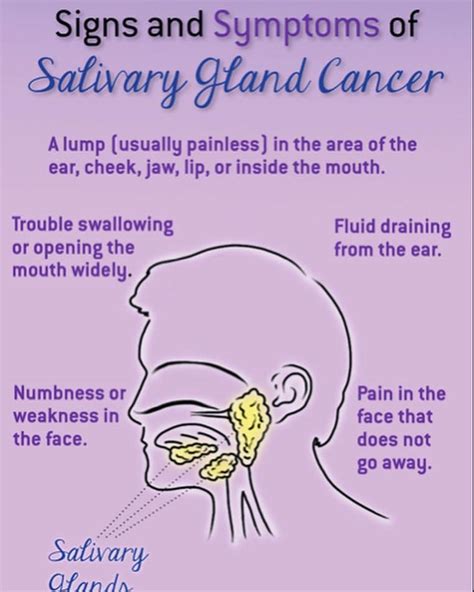
Cancerous growths in the salivary glands can interfere with the normal functioning of the mouth and throat, leading to difficulties in swallowing and speaking. You may experience a feeling of something being stuck in your throat, have trouble swallowing solid foods or liquids, or notice changes in your voice. These symptoms should not be ignored and should prompt a visit to your healthcare provider.
5. Changes in Saliva Production

The salivary glands are responsible for producing saliva, which helps with digestion and keeps the mouth moist. Any changes in the amount or consistency of saliva can be a cause for concern. If you notice a sudden decrease in saliva production, an increase in saliva production (drooling), or changes in the color or texture of your saliva, it is important to discuss these symptoms with your doctor.
Understanding the Risk Factors
While anyone can develop salivary gland cancer, certain factors may increase the risk. These include:
- Age: The risk of salivary gland cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over the age of 50.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, especially in the head and neck region, can increase the likelihood of developing salivary gland cancer.
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including salivary gland cancer.
- Family History: A family history of salivary gland cancer or other types of cancer can slightly elevate the risk.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Certain strains of HPV have been associated with an increased risk of salivary gland cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms or have concerns about your salivary glands, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They may perform a physical examination, order imaging tests (such as CT scans or MRI), and possibly recommend a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
Treatment for salivary gland cancer depends on the stage and location of the tumor. Common approaches include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells, and chemotherapy to prevent the spread of cancer. In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be necessary.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
While salivary gland cancer cannot always be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce your overall cancer risk. Here are some recommendations:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for various cancers, including salivary gland cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly lower your chances of developing cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake has been linked to an increased risk of cancer. Moderating your alcohol consumption can be beneficial for your overall health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can contribute to cancer prevention.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular dental check-ups, can help detect any changes or abnormalities in the mouth and salivary glands early on.
Conclusion
Salivary gland cancer, although rare, can have serious implications if left undetected or untreated. By being aware of the early-stage signs and symptoms, you can take an active role in your health and seek timely medical attention. Remember, early detection is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes. Stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
FAQ

What are the survival rates for salivary gland cancer?

+
Survival rates for salivary gland cancer vary depending on the stage and type of cancer. Early-stage cancers have higher survival rates, while advanced-stage cancers may have lower survival rates. It’s important to consult with a medical professional for an accurate assessment of your specific situation.
Can salivary gland cancer spread to other parts of the body?

+
Yes, salivary gland cancer can spread to other parts of the body, especially if left untreated or detected at a later stage. It is crucial to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the spread and manage the cancer effectively.
Are there any alternative treatments for salivary gland cancer?
+
While conventional treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are the primary approaches for salivary gland cancer, some individuals may explore complementary therapies alongside medical treatment. It’s important to discuss any alternative treatments with your healthcare team to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific case.