17 Calcium Storage Locations: Essential Facts You Need To Know

Calcium Storage Locations: Unveiling the Secrets of Calcium's Journey

Calcium, an essential mineral, plays a pivotal role in our bodies, and understanding its storage locations is crucial. From maintaining strong bones to facilitating vital physiological processes, calcium's presence is felt throughout our anatomy. In this blog, we will explore the 17 key calcium storage locations, shedding light on their significance and the intricate network that ensures our bodies function optimally.
The Calcium Odyssey: A Journey Through the Body

Calcium, an essential mineral for life, is stored in various locations throughout the body, each serving a unique purpose. This mineral is not just a building block for strong bones; it's a key player in muscle function, nerve transmission, and even blood clotting. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the 17 primary storage locations of calcium and their importance.
1. Bones and Teeth: The Calcium Fortress

The most prominent calcium storage location is, without a doubt, our bones and teeth. Approximately 99% of the body's calcium is stored here, making it the primary reservoir. This calcium is vital for structural support, providing strength and rigidity to our skeletal system. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in dental health, ensuring strong and healthy teeth.
2. Blood: The Calcium Highway

While a smaller percentage of calcium is found in the blood, its role is no less significant. Calcium in the blood, known as serum calcium, is responsible for vital physiological processes. It aids in muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood clotting. A delicate balance of calcium in the blood is essential, and any disruption can lead to serious health issues.
Sub-locations:

- Plasma: Calcium in the plasma helps maintain the body’s acid-base balance and is crucial for muscle and nerve function.
- Red Blood Cells: These cells store a small amount of calcium, which is important for their shape and function.
3. Soft Tissues: The Calcium Reserve

Calcium is also found in various soft tissues throughout the body, including muscles, skin, and organs. While the concentration is lower compared to bones and blood, these soft tissues act as a reserve, releasing calcium when needed. This ensures a constant supply for vital physiological processes, especially during times of low dietary intake or increased demand.
4. Extracellular Fluid: The Calcium Pool
Extracellular fluid, which includes the fluid between cells and in the lymphatic system, contains a small amount of calcium. This calcium pool is crucial for maintaining the body's overall calcium balance. It ensures a continuous supply of calcium to various body parts, especially when bone calcium is not readily available.
5. Intracellular Fluid: The Calcium Partner

Intracellular fluid, found within cells, also contains calcium. This calcium works in tandem with the calcium in extracellular fluid to regulate various cellular processes. It is particularly important for muscle and nerve cells, where calcium ions play a critical role in muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission.
6. Mitochondria: The Calcium Powerhouse

Mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are unique organelles that store calcium. This calcium is essential for energy production and cellular respiration. It also plays a role in regulating cellular processes, making mitochondria a key player in maintaining overall cellular health.
7. Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Calcium Network
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes within cells that serves various functions, including protein synthesis and calcium storage. Calcium in the ER is crucial for proper cell function and plays a role in various cellular processes, including muscle contraction and cell signaling.
8. Golgi Apparatus: The Calcium Processor

The Golgi apparatus, a complex network of membranes, is responsible for processing and packaging proteins and lipids. It also stores and releases calcium, which is essential for its proper functioning. Calcium in the Golgi apparatus is involved in various cellular processes, including protein modification and secretion.
9. Nucleus: The Calcium Guardian
The nucleus, the control center of the cell, also stores a small amount of calcium. This calcium is essential for maintaining the structure and function of the nucleus, as well as for regulating various cellular processes. It plays a crucial role in DNA replication and gene expression, ensuring the proper functioning of the cell.
10. Cell Membrane: The Calcium Gateway
The cell membrane, which surrounds each cell, contains a small amount of calcium. This calcium is essential for maintaining the membrane's structure and function. It also plays a role in cell signaling, acting as a gateway for calcium ions to enter and exit the cell, thereby regulating various cellular processes.
11. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum: The Calcium Reservoir
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a specialized form of the endoplasmic reticulum found in muscle cells. It stores a significant amount of calcium, which is essential for muscle contraction. When a muscle cell receives a signal to contract, calcium is released from the SR, triggering a cascade of events that lead to muscle contraction.
12. Cardiac Muscle: The Calcium Conductor
Cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart, has a unique calcium storage and release mechanism. Calcium is stored in the SR of cardiac muscle cells and is released in a controlled manner to initiate heart muscle contraction. This process is crucial for maintaining a regular heartbeat and ensuring the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system.
13. Skeletal Muscle: The Calcium Engine
Skeletal muscle, which attaches to bones and enables movement, also stores calcium. Similar to cardiac muscle, calcium is stored in the SR of skeletal muscle cells and is released during muscle contraction. This process is vital for movement and physical activity, as it provides the necessary force for muscle contraction.
14. Smooth Muscle: The Calcium Regulator
Smooth muscle, found in various organs and structures such as blood vessels, the digestive tract, and the uterus, also stores calcium. Calcium in smooth muscle plays a crucial role in regulating muscle tone and contraction. It is essential for maintaining blood flow, digestive processes, and reproductive functions.
15. Brain: The Calcium Thinker
The brain, our body's control center, also stores calcium. Calcium in the brain is essential for proper neurological function, including neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity. It plays a critical role in learning, memory, and cognitive function, making it a key player in our overall brain health.
16. Nervous System: The Calcium Communicator
The nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, also stores calcium. Calcium ions are crucial for the transmission of nerve impulses, allowing for communication between different parts of the body. They play a vital role in sensory perception, movement, and the coordination of various physiological processes.
17. Blood Cells: The Calcium Carriers
Blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, also store calcium. While the concentration is relatively low, calcium in blood cells is essential for their proper function. For example, calcium in red blood cells helps maintain their shape and flexibility, while calcium in platelets is crucial for blood clotting.
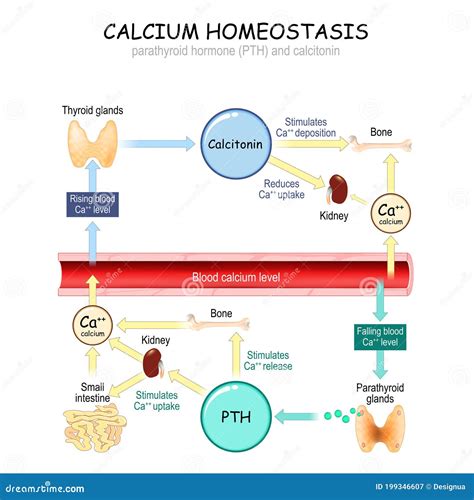
The Importance of Calcium Balance
Maintaining a proper balance of calcium in the body is crucial for overall health. Imbalances can lead to a range of health issues, including osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Ensuring an adequate intake of calcium-rich foods and, if necessary, supplements, is essential for maintaining optimal health.
FAQs
What happens if I have too much calcium in my body?

+
Excess calcium in the body, a condition known as hypercalcemia, can lead to various health issues. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, nausea, and even kidney stones. It's important to maintain a balanced diet and, if necessary, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Can a calcium deficiency impact my overall health?

+
Absolutely. Calcium deficiency, or hypocalcemia, can lead to weak bones, increased risk of fractures, and even neurological symptoms. It's crucial to ensure an adequate intake of calcium-rich foods and, if necessary, consult a healthcare professional for guidance on supplementation.
What are some good sources of calcium?

+
Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are excellent sources of calcium. Leafy green vegetables, such as kale and broccoli, are also rich in calcium. For those who are lactose intolerant or follow a vegan diet, calcium-fortified plant-based milk and tofu are good alternatives.
Conclusion
Understanding the various calcium storage locations in the body is crucial for maintaining optimal health. From our bones and teeth to our blood, muscles, and even our brain, calcium plays a vital role in numerous physiological processes. By ensuring a balanced diet and, if necessary, taking supplements, we can maintain a healthy calcium balance and support our overall well-being.
💡 Note: This blog provides a general overview of calcium storage locations. For personalized advice on calcium intake and supplementation, consult a healthcare professional.