2. 7 Ultimate Guide To Piping Mastery Now!

Unleashing Your Potential in Piping: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to the world of piping, an essential yet often overlooked aspect of various industries. Whether you're a beginner eager to learn the basics or an experienced professional seeking to refine your skills, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools to excel in the art of piping.
Piping is an intricate system of tubes and pipes that transport fluids, gases, and even solids from one point to another. It plays a crucial role in numerous sectors, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and even water treatment. A well-designed and maintained piping system ensures efficient and safe operations, making it a critical component in modern industrial processes.
Understanding the Basics of Piping

Before delving into the intricacies of piping, it's essential to grasp the fundamental concepts that form the foundation of this field.
What is Piping?

Piping refers to the arrangement of pipes, tubes, fittings, and components that form a system to convey fluids or gases. These systems are designed to meet specific requirements, such as fluid flow rate, pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility.
Key Components of a Piping System

- Pipes and Tubes: These are the primary conduits that carry the fluid or gas. Pipes are typically cylindrical and made from various materials like steel, copper, or plastic, while tubes are often seamless and used for more specialized applications.
- Fittings: Fittings are used to connect pipes and tubes, change direction, or alter the size of the piping system. Common fittings include elbows, tees, couplings, and valves.
- Valves: Valves control the flow of fluids within the piping system. They can be used to start, stop, or regulate the flow, and are an essential safety feature in many applications.
- Supports and Hangers: These components are used to support the weight of the piping system and maintain its alignment. They include clamps, hangers, and supports that are designed to withstand the forces exerted by the fluid or gas.
The Importance of Piping Design

Piping design is a critical aspect of any industrial project. A well-designed piping system ensures the safe and efficient transportation of fluids, while also minimizing the risk of leaks, blockages, or other issues that could lead to costly downtime or safety hazards.
Key Considerations in Piping Design

- Fluid Properties: The properties of the fluid being transported, such as its temperature, pressure, and chemical composition, must be carefully considered during the design process. These factors influence the selection of materials, pipe sizes, and other design parameters.
- Process Requirements: Piping systems must be designed to meet the specific requirements of the process they serve. This includes considerations such as flow rates, pressure drops, and the need for specialized components like heat exchangers or filters.
- Safety and Code Compliance: Piping design must adhere to industry standards and regulations to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. This includes considerations such as pressure ratings, material compatibility, and the use of appropriate valves and fittings.
- Layout and Routing: The layout and routing of the piping system should be optimized to minimize the risk of leaks, ensure easy access for maintenance, and avoid interference with other equipment or structures.
Piping Materials and Their Selection

The choice of piping materials is a critical decision that can impact the performance, longevity, and safety of the entire system. Different materials have unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications.
Common Piping Materials

- Carbon Steel: Carbon steel is a popular choice for piping systems due to its strength, durability, and relatively low cost. It is commonly used in applications involving high-pressure and high-temperature fluids.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and is often used in applications where the fluid is corrosive or contains solid particles. It is more expensive than carbon steel but offers superior performance in certain environments.
- Copper: Copper is a popular choice for water supply and heating systems due to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It is also commonly used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- Plastic (PVC, CPVC, PE, etc.): Plastic pipes are lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion. They are commonly used in low-pressure applications such as water distribution, drainage, and sewage systems.
Factors Influencing Material Selection

- Fluid Properties: The properties of the fluid being transported, such as its temperature, pressure, and chemical composition, are critical factors in material selection. Some materials may be more resistant to certain chemicals or able to withstand higher temperatures or pressures.
- Corrosion Resistance: The risk of corrosion must be carefully considered, especially in applications where the fluid is corrosive or contains solid particles. Materials with excellent corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel or certain types of plastic, may be required.
- Cost: The cost of the material is an important consideration, especially in large-scale projects. While some materials may be more expensive upfront, they may offer long-term cost savings due to their durability or reduced maintenance requirements.
- Availability and Sourcing: The availability and ease of sourcing a particular material can also influence the selection process. Some materials may be more readily available or have a shorter lead time, making them a more practical choice for certain projects.
Piping Installation and Maintenance
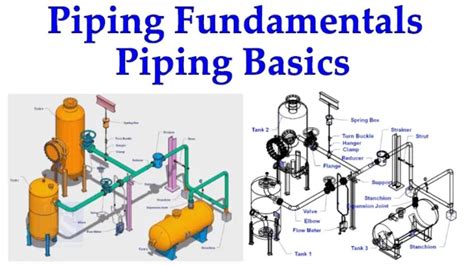
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensuring the reliability and longevity of a piping system. Whether you're working on a new project or maintaining an existing system, attention to detail and adherence to best practices are essential.
Installation Best Practices

- Follow Industry Standards: Adhere to recognized industry standards and codes, such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) B31 series of codes, which provide guidelines for the design, installation, and testing of piping systems.
- Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control measures during installation to ensure that all components are properly installed and meet the required specifications. This includes regular inspections and testing of the system.
- Proper Support and Alignment: Ensure that the piping system is properly supported and aligned to prevent excessive stress on the pipes and fittings. Use appropriate supports and hangers to maintain the integrity of the system.
- Welding and Joining Techniques: If welding or other joining techniques are required, ensure that the work is carried out by qualified personnel and in accordance with relevant standards. Proper welding procedures and quality control measures are essential to ensure the integrity of the joints.
Maintenance and Inspection

- Regular Inspections: Develop a comprehensive inspection and maintenance program to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems. Regular inspections should include visual checks for leaks, corrosion, or other signs of wear and tear.
- Corrosion Monitoring: Implement corrosion monitoring programs to detect and mitigate corrosion-related issues. This may involve the use of corrosion coupons, inline monitors, or other advanced techniques to assess the condition of the piping system.
- Leak Detection: Use appropriate leak detection methods to identify and repair leaks promptly. This may involve the use of ultrasonic detectors, infrared cameras, or other specialized equipment.
- Valve Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain valves to ensure they are functioning properly. This includes testing the operation of valves, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn-out seals or gaskets as needed.
Piping Systems in Different Industries

Piping systems are used in a wide range of industries, each with its own unique requirements and challenges. Understanding the specific needs of these industries is crucial for designing and maintaining effective piping systems.
Oil and Gas Industry

- Piping systems in the oil and gas industry must be designed to handle high-pressure and high-temperature fluids, often in corrosive environments. Materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel are commonly used, along with specialized alloys for extreme conditions.
- Safety is a critical concern in the oil and gas industry, and piping systems must be designed and maintained to minimize the risk of leaks, fires, or other hazards. This includes the use of pressure relief valves, fire protection systems, and rigorous inspection and maintenance programs.
Chemical Processing Industry

- The chemical processing industry often involves the handling of corrosive or hazardous fluids. Piping systems must be designed to withstand these harsh conditions, with materials carefully selected to ensure compatibility and corrosion resistance.
- Process control is a key consideration in chemical processing. Piping systems must be designed to maintain precise flow rates, pressures, and temperatures to ensure the quality and safety of the products being manufactured.
Power Generation Industry

- Piping systems in power plants must be designed to handle high-pressure steam and other fluids used in the generation of electricity. Materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel are commonly used, along with specialized alloys for high-temperature applications.
- Safety and reliability are critical in power generation. Piping systems must be designed and maintained to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the plant, with regular inspections and maintenance to identify and address potential issues.
Conclusion

Piping is a critical component in numerous industries, and mastering the art of piping requires a deep understanding of its fundamentals, design principles, and maintenance practices. Whether you're designing a new system or maintaining an existing one, attention to detail and adherence to best practices are essential to ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of the piping system.
By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you'll be well on your way to becoming a piping expert. Remember, the key to success in piping is a combination of technical knowledge, practical experience, and a commitment to safety and quality. With these foundations in place, you'll be able to tackle any piping challenge that comes your way.
FAQ

What are the key considerations when selecting piping materials?
+When selecting piping materials, key considerations include fluid properties (temperature, pressure, and chemical composition), corrosion resistance, cost, and availability. Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications.
How often should piping systems be inspected and maintained?
+The frequency of inspections and maintenance depends on the specific application and industry standards. However, as a general guideline, regular inspections should be conducted at least annually, with more frequent inspections in high-risk or critical applications.
What are some common challenges in piping design and how can they be addressed?
+Common challenges in piping design include meeting fluid flow requirements, ensuring proper support and alignment, and selecting the right materials. These challenges can be addressed by following industry standards, conducting thorough engineering calculations, and collaborating with experienced professionals.
What are some best practices for welding and joining techniques in piping installation?
+Best practices for welding and joining techniques include using qualified personnel, following industry standards and codes, implementing quality control measures, and ensuring proper pre- and post-weld cleaning and inspection.
How can I stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and best practices in the field of piping?
+To stay current with the latest advancements and best practices in piping, consider joining professional organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the International Society of Automation (ISA). These organizations offer access to industry publications, conferences, and training opportunities.
📖 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of piping, but it is important to consult industry-specific standards and regulations for detailed guidance on piping design, installation, and maintenance.

