6 Tips To Design The Ultimate Medical Anthropology Guide Today

Unveiling the Intricacies of Medical Anthropology: A Comprehensive Guide

Medical anthropology is an interdisciplinary field that explores the fascinating interplay between health, culture, and society. By delving into the diverse beliefs, practices, and experiences of different communities, medical anthropologists offer valuable insights into the complexities of human health and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a journey to understand the fundamentals of medical anthropology, its methodologies, and its profound impact on healthcare systems worldwide.
Understanding the Foundation of Medical Anthropology

Medical anthropology stands at the intersection of anthropology, medicine, and public health, offering a unique perspective on the cultural dimensions of health and illness. It delves into the social, cultural, and biological factors that shape human health, challenging conventional medical models and promoting a holistic understanding of well-being.
At its core, medical anthropology is concerned with the ways in which cultural beliefs, practices, and social structures influence health outcomes and healthcare delivery. By examining the cultural context of health, medical anthropologists reveal the intricate relationship between illness, healing, and the broader social fabric.
Key Concepts and Theories in Medical Anthropology

To grasp the complexities of medical anthropology, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with its key concepts and theories. Here are some fundamental concepts that underpin the field:
- Biocultural Approach: This perspective emphasizes the interconnectedness of biological and cultural factors in shaping health and illness. It recognizes that health is not solely determined by biological processes but is also influenced by cultural beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Cultural Competence: Cultural competence refers to the ability of healthcare professionals to understand and respect the cultural beliefs and practices of their patients. It involves recognizing and addressing cultural barriers to healthcare access and delivery, ensuring that care is culturally appropriate and effective.
- Social Determinants of Health: Medical anthropology acknowledges the significant impact of social factors on health outcomes. These determinants include socioeconomic status, education, access to healthcare, and environmental conditions, all of which can influence an individual's health and well-being.
- Emic and Etic Perspectives: Emic perspectives focus on understanding health and illness from the insider's point of view, exploring the local meanings and interpretations of health-related phenomena. Etic perspectives, on the other hand, involve an outsider's analytical framework, allowing for comparative analysis and generalization across different cultural contexts.
Exploring Methodologies in Medical Anthropology
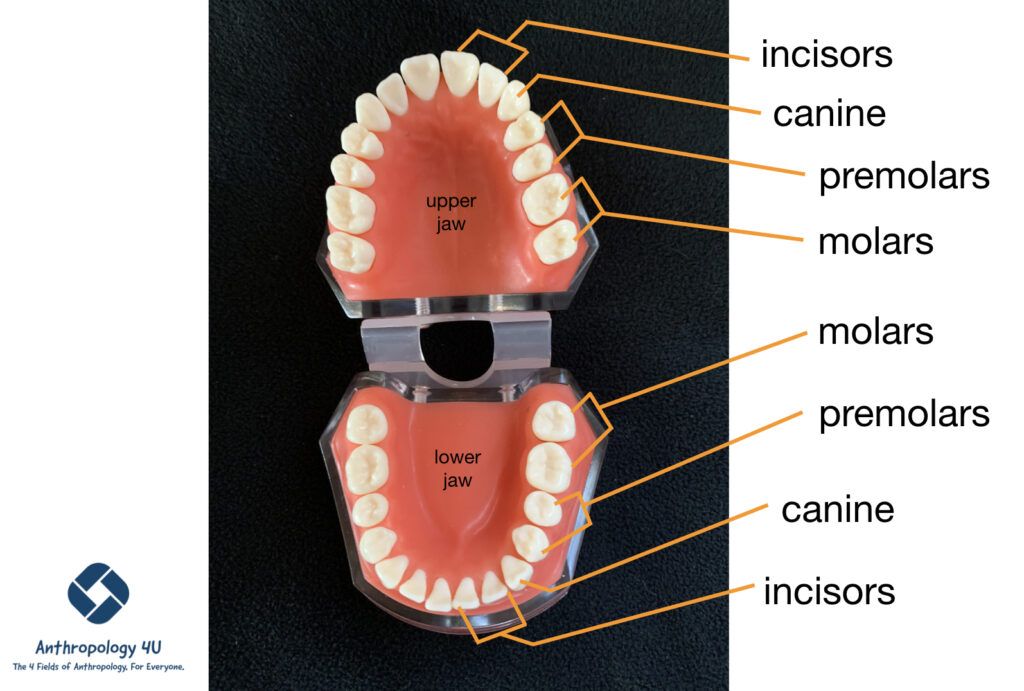
Medical anthropologists employ a range of methodologies to gather data and gain insights into the cultural dimensions of health. These methodologies include both qualitative and quantitative approaches, often combined to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Qualitative Methods

- Participant Observation: This method involves immersing oneself in the community or cultural group being studied, observing and participating in their daily lives. Participant observation allows anthropologists to gain first-hand knowledge of cultural practices, beliefs, and behaviors related to health and illness.
- In-Depth Interviews: Through in-depth interviews, anthropologists engage in open-ended conversations with individuals or groups, exploring their perspectives, experiences, and beliefs about health and illness. These interviews provide rich, contextualized data that captures the cultural nuances of health.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a small group of individuals with shared experiences or characteristics to discuss a specific topic. This method facilitates the exploration of common themes, beliefs, and practices related to health within a particular cultural or social group.
Quantitative Methods

- Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires are used to collect data from a larger sample of individuals, often through self-report measures. These methods allow anthropologists to gather quantitative data on health-related beliefs, behaviors, and outcomes, providing a broader perspective on cultural patterns and trends.
- Secondary Data Analysis: Anthropologists may also analyze existing data, such as demographic information, health records, or census data, to explore the relationship between cultural factors and health outcomes. This method allows for the identification of patterns and trends that may not be apparent through qualitative research alone.
Applying Medical Anthropology in Healthcare

The insights and knowledge gained through medical anthropology have profound implications for healthcare systems and practices. By understanding the cultural dimensions of health, medical anthropologists can contribute to the development of more effective and culturally sensitive healthcare interventions.
Cultural Competence in Healthcare

Medical anthropologists play a crucial role in promoting cultural competence among healthcare professionals. By educating healthcare providers about the cultural beliefs and practices of their patients, anthropologists help ensure that care is delivered in a way that is respectful, sensitive, and effective. This approach improves patient-provider communication, enhances trust, and ultimately leads to better health outcomes.
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Medical anthropology provides valuable insights into the cultural factors that influence health behaviors and practices. By understanding these factors, anthropologists can develop culturally tailored health promotion and disease prevention programs. These initiatives aim to empower individuals and communities to make informed choices about their health, promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing the burden of disease.
Addressing Health Disparities

Medical anthropology plays a vital role in identifying and addressing health disparities among different cultural and social groups. By uncovering the cultural and structural barriers to healthcare access and utilization, anthropologists can inform the development of targeted interventions and policies aimed at reducing health inequalities.
The Impact of Medical Anthropology on Global Health

The contributions of medical anthropology extend far beyond individual healthcare settings. Its impact is felt at the global level, shaping international health policies and initiatives. By providing a cultural lens through which to view health and illness, medical anthropology offers valuable insights into the complexities of global health challenges.
Global Health Initiatives

Medical anthropologists contribute to the design and implementation of global health initiatives by considering the cultural context of health issues. They help ensure that interventions are culturally appropriate, acceptable, and effective, increasing the likelihood of success and sustainability.
Understanding Cultural Barriers to Healthcare

In many parts of the world, cultural beliefs and practices can present significant barriers to healthcare access and utilization. Medical anthropologists play a crucial role in identifying and addressing these barriers, working with local communities to develop culturally sensitive solutions that promote equitable access to healthcare services.
Promoting Cultural Sensitivity in Healthcare

By highlighting the importance of cultural sensitivity in healthcare, medical anthropology encourages healthcare providers and organizations to adopt a more holistic and patient-centered approach. This shift in perspective can lead to improved patient experiences, increased trust in healthcare systems, and better health outcomes for diverse populations.
Conclusion

Medical anthropology offers a unique and invaluable perspective on the cultural dimensions of health and illness. By exploring the intricate relationship between culture, society, and health, medical anthropologists provide insights that shape healthcare practices, policies, and global health initiatives. Through its interdisciplinary nature and focus on cultural competence, medical anthropology contributes to a more equitable, effective, and culturally sensitive healthcare system.
What is the main focus of medical anthropology?

+
Medical anthropology focuses on the cultural, social, and biological factors that influence health and illness. It explores the ways in which cultural beliefs, practices, and social structures shape healthcare practices and outcomes.
How does medical anthropology contribute to healthcare practices?

+
Medical anthropology contributes to healthcare practices by promoting cultural competence among healthcare professionals. It helps ensure that care is delivered in a way that is respectful, sensitive, and effective, leading to improved patient-provider communication and better health outcomes.
What are some key methodologies used in medical anthropology research?
+Medical anthropologists employ a range of methodologies, including participant observation, in-depth interviews, focus groups, surveys, and secondary data analysis. These methods allow them to gather qualitative and quantitative data on the cultural dimensions of health.
How does medical anthropology address health disparities?
+Medical anthropology plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing health disparities by uncovering the cultural and structural barriers to healthcare access and utilization. It informs the development of targeted interventions and policies aimed at reducing health inequalities.
What is the impact of medical anthropology on global health initiatives?
+Medical anthropology contributes to global health initiatives by providing a cultural lens through which to view health issues. It ensures that interventions are culturally appropriate, acceptable, and effective, leading to more successful and sustainable outcomes.


