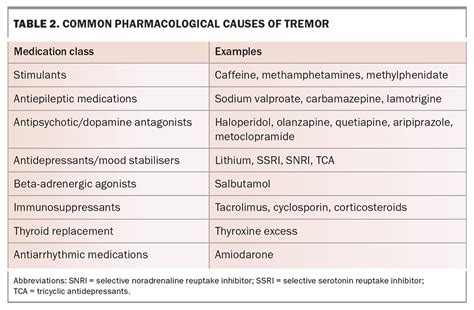
Essential Tremor Vs Parkinsonian Tremor: Expert Guide To Differentiating

Tremors are involuntary, rhythmic movements that can affect various parts of the body. While tremors are a common symptom associated with neurological disorders, not all tremors are the same. Understanding the differences between essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key characteristics, causes, and diagnostic criteria of these two distinct types of tremors. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of the differences and be better equipped to differentiate between essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor.
Understanding Essential Tremor

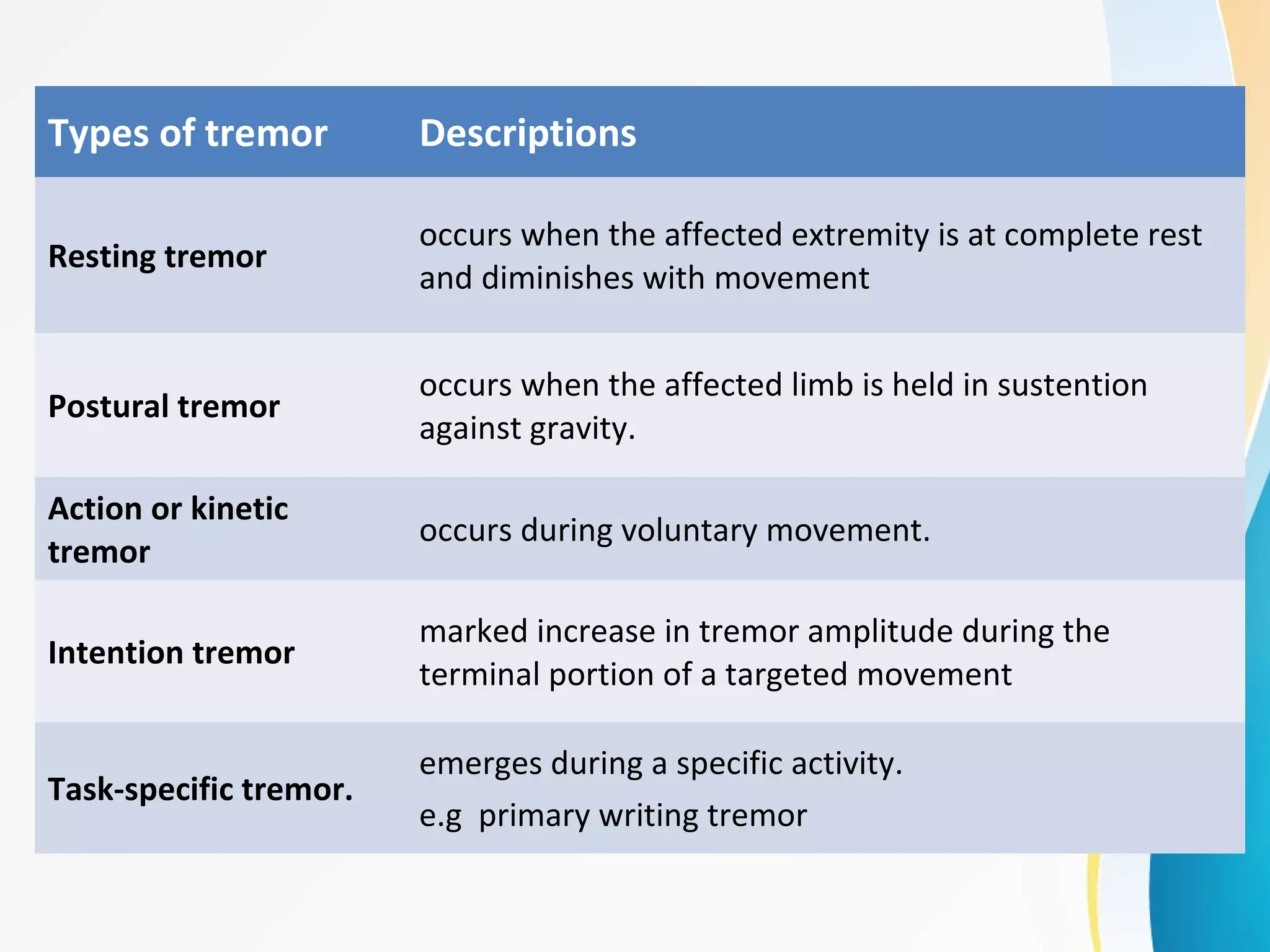
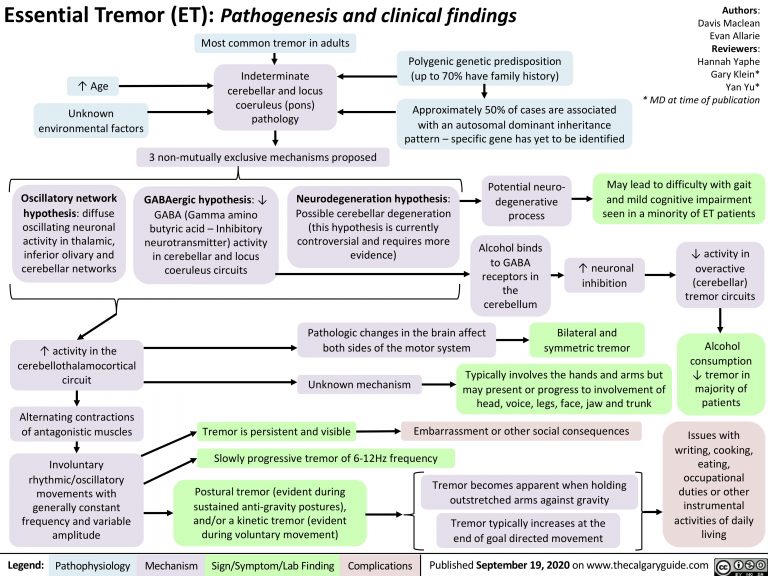
Essential tremor, also known as benign essential tremor, is one of the most common movement disorders. It is characterized by involuntary shaking or trembling, typically affecting the hands and arms. However, essential tremor can also involve other body parts, such as the head, voice, and legs.
Key Characteristics of Essential Tremor

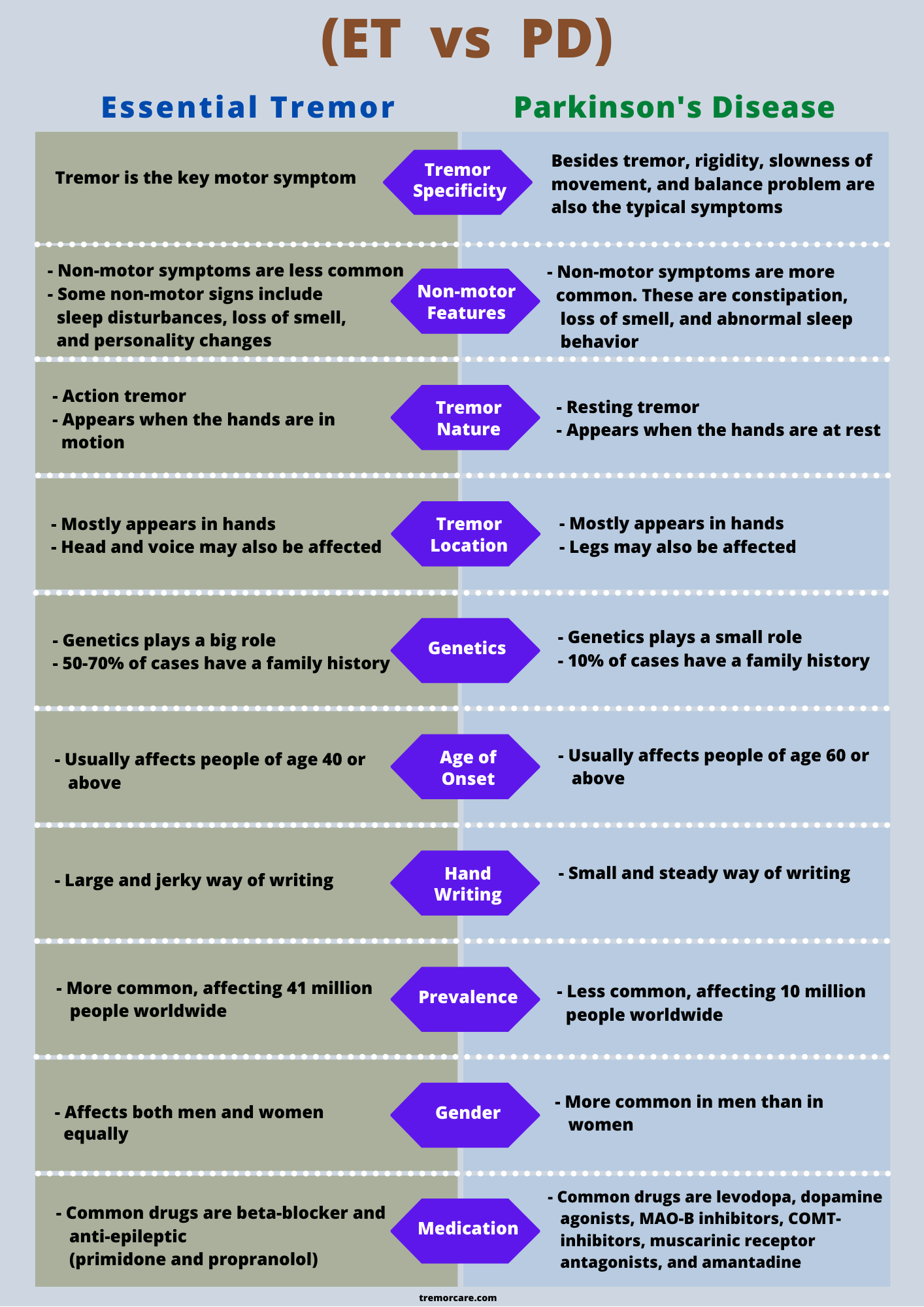
- Postural and Kinetic Tremor: Essential tremor typically presents as a postural tremor, occurring when maintaining a specific posture or position. It can also manifest as a kinetic tremor, which occurs during voluntary movements.
- Frequency and Amplitude: The tremor associated with essential tremor has a frequency of 4-12 Hz and is often described as a high-frequency, low-amplitude tremor.
- Worsens with Age: Essential tremor tends to worsen with age, and the severity of tremors can vary from person to person.
- Family History: There is a strong genetic component to essential tremor, with a higher prevalence among individuals with a family history of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of essential tremor is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve abnormalities in the cerebellum and its connections with other brain regions. Risk factors for essential tremor include:
- Genetics: Essential tremor often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Age: The risk of developing essential tremor increases with age.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as antidepressants and stimulants, can trigger or worsen tremors.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development or exacerbation of essential tremor.
Parkinsonian Tremor: A Distinct Type

Parkinsonian tremor is a symptom of Parkinson's disease, a progressive neurological disorder. It is characterized by a specific type of tremor that has unique features and is often the earliest sign of Parkinson's disease.
Key Characteristics of Parkinsonian Tremor
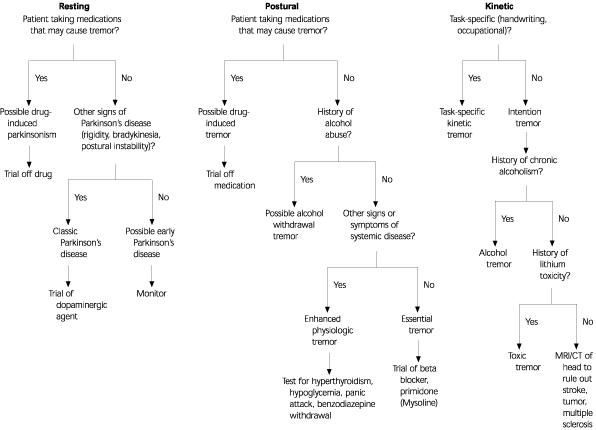
- Resting Tremor: Unlike essential tremor, Parkinsonian tremor is primarily a resting tremor, occurring when the affected body part is at rest and not performing any voluntary movements.
- Frequency and Amplitude: Parkinsonian tremor has a lower frequency (3-6 Hz) compared to essential tremor and is typically described as a low-frequency, high-amplitude tremor.
- Asymmetry: Parkinsonian tremor often starts on one side of the body and may progress to involve the other side over time.
- Associated Symptoms: Parkinsonian tremor is usually accompanied by other symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as stiffness, slowness of movement, and balance problems.
Causes and Pathophysiology
Parkinsonian tremor is caused by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain responsible for controlling movement. The loss of dopamine leads to an imbalance in the brain's motor control system, resulting in the characteristic tremor and other motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Differentiating Essential Tremor and Parkinsonian Tremor

Distinguishing between essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Here are some key differences to consider:
| Characteristic | Essential Tremor | Parkinsonian Tremor |
|---|---|---|
| Tremor Type | Postural and kinetic tremor | Resting tremor |
| Frequency | 4-12 Hz | 3-6 Hz |
| Amplitude | Low | High |
| Symmetry | Often symmetrical | Initially asymmetrical |
| Associated Symptoms | Tremor is usually the only symptom | Tremor accompanied by other Parkinson's symptoms |

Diagnostic Criteria
To differentiate between essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor, healthcare professionals may consider the following criteria:
- The presence of resting tremor is a strong indicator of Parkinson's disease.
- The presence of other Parkinson's symptoms, such as bradykinesia (slowness of movement) and rigidity, supports a diagnosis of Parkinsonian tremor.
- The absence of other Parkinson's symptoms and a family history of tremor may suggest essential tremor.
- Neuroimaging studies, such as MRI or PET scans, can be helpful in ruling out other conditions and confirming the diagnosis.
Management and Treatment Options
The management and treatment of essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor differ based on the underlying condition.
Essential Tremor Management

- Lifestyle Modifications: Reducing stress, avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol, and practicing relaxation techniques can help manage essential tremor.
- Medications: Beta-blockers, such as propranolol, and anticonvulsant medications are commonly prescribed to reduce tremor severity.
- Botox Injections: Botox injections can be effective in treating localized tremors, particularly in the hands and head.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): In severe cases, DBS may be considered as a surgical option to control tremors.
Parkinsonian Tremor Treatment

- Dopaminergic Medications: Levodopa and dopamine agonists are the primary medications used to treat Parkinson's disease and alleviate tremor symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve movement and balance, as well as manage associated symptoms.
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy may be beneficial for managing speech and swallowing difficulties associated with Parkinson's disease.
- Surgical Options: In advanced cases of Parkinson's disease, surgical procedures such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) or lesioning may be considered to control tremors and other motor symptoms.
Living with Tremors

Living with tremors, whether essential tremor or Parkinsonian tremor, can present challenges in daily life. However, with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
Tips for Managing Tremors

- Seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and online communities to share experiences and learn coping strategies.
- Modify daily activities and adapt your environment to accommodate tremors. For example, using weighted utensils or wearing wrist weights can help stabilize movements.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and manage tremor severity.
- Stay physically active and engage in regular exercise to maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
Conclusion

Differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. While both conditions involve tremors, they have distinct characteristics, causes, and associated symptoms. By understanding the key differences and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can receive the necessary support and treatment to manage their tremors and improve their quality of life.
Can essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor occur together?

+
Yes, it is possible for individuals to have both essential tremor and Parkinsonian tremor. In such cases, the tremors may have different characteristics and may require a combination of treatment approaches.
Are there any natural remedies for managing tremors?

+
While natural remedies may provide some relief, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments. Some natural remedies that may help manage tremors include herbal supplements, acupuncture, and yoga.
Can tremors be cured completely?
+Currently, there is no cure for essential tremor or Parkinson’s disease. However, with proper management and treatment, tremors can be effectively controlled, allowing individuals to maintain a good quality of life.