How To Become An Anesthesiology

Introduction to the Field of Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology is a fascinating and critical branch of medicine that focuses on the administration of anesthesia, pain management, and the overall well-being of patients during surgical procedures and critical care. Anesthesiologists play a vital role in ensuring patient safety and comfort, making it a highly respected and rewarding medical specialty. If you’re considering a career in anesthesiology, this guide will provide you with the necessary steps and insights to help you achieve your professional goals.
Understanding the Role of an Anesthesiologist
Anesthesiologists are medical doctors who specialize in anesthesia, which involves the use of medications to induce a temporary loss of sensation or consciousness during medical procedures. They are responsible for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Preoperative Assessment: Evaluating patients’ medical histories, conducting physical examinations, and determining the most suitable anesthesia plan.
- Anesthesia Administration: Delivering anesthesia medications safely and effectively to ensure patients remain comfortable and pain-free throughout surgical procedures.
- Pain Management: Providing pain relief and managing chronic pain conditions using various techniques and medications.
- Critical Care: Monitoring and stabilizing patients in intensive care units, ensuring their vital signs are within normal ranges.
- Anesthesia Equipment Management: Maintaining and operating anesthesia machines and related equipment.
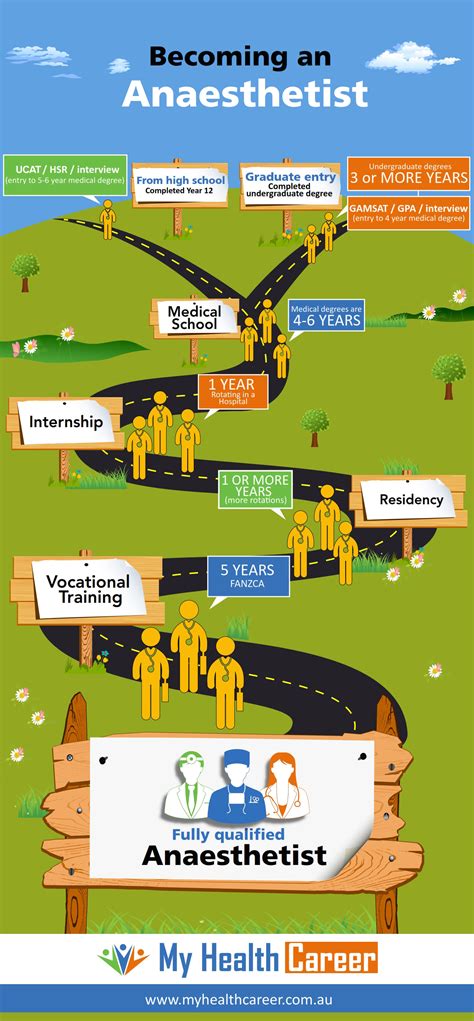
Educational Pathway to Becoming an Anesthesiologist

Becoming an anesthesiologist requires a significant commitment to education and training. Here’s an overview of the steps you’ll need to take:
Step 1: Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree

The first step towards a career in anesthesiology is to earn a bachelor’s degree. While there is no specific undergraduate major required, it is recommended to pursue a science-related field such as biology, chemistry, or pre-med. During your undergraduate studies, focus on maintaining a strong GPA and gaining relevant experience through research, internships, or volunteer work.
Step 2: Medical School
After completing your bachelor’s degree, you must attend medical school to earn a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree. Medical school typically takes four years to complete and provides a comprehensive education in the basic and clinical sciences. During this time, you’ll gain a deep understanding of human anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and medical ethics.
Step 3: Residency Training

Following medical school, you’ll need to complete a residency program in anesthesiology. Residency programs typically last four years and provide hands-on training and experience in various aspects of anesthesiology. During your residency, you’ll work under the supervision of experienced anesthesiologists, gaining skills in anesthesia administration, pain management, and critical care.
Step 4: Board Certification

To become a fully licensed anesthesiologist, you must obtain board certification from the American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA) or the American Osteopathic Board of Anesthesiology (AOBA). This involves passing a series of written and oral examinations that assess your knowledge and clinical skills in anesthesiology. Board certification is a highly regarded achievement and is often required for employment and advancement in the field.
Specialty Options in Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology offers several specialty options that allow you to focus on specific areas of interest. Some of the popular specialties include:
- Cardiac Anesthesiology: Focusing on providing anesthesia and critical care for patients undergoing cardiac surgeries.
- Neuroanesthesiology: Specializing in anesthesia and pain management for neurosurgical procedures.
- Pediatric Anesthesiology: Caring for children and adolescents requiring anesthesia and pain management.
- Obstetric Anesthesiology: Providing anesthesia and pain relief for women during childbirth and gynecological procedures.
- Critical Care Medicine: Managing patients in intensive care units, ensuring their vital functions are stabilized.
Skills and Attributes for Success in Anesthesiology
To excel in the field of anesthesiology, certain skills and attributes are essential:
- Strong Medical Knowledge: A solid understanding of anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology is crucial for making informed decisions regarding anesthesia administration.
- Attention to Detail: Anesthesiologists must pay close attention to detail to ensure the accurate administration of medications and the proper functioning of anesthesia equipment.
- Critical Thinking: The ability to think critically and make quick decisions is vital, especially in emergency situations.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication with patients, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals is essential for building trust and ensuring patient safety.
- Empathy and Compassion: Anesthesiologists should possess a caring and empathetic nature, as they often work with patients who are anxious or in pain.
- Physical Stamina: The job can be physically demanding, requiring long hours on your feet and the ability to handle stressful situations.
Steps to Prepare for a Career in Anesthesiology

If you’re considering a career in anesthesiology, here are some steps you can take to prepare:
- Shadow an Anesthesiologist: Arrange opportunities to shadow experienced anesthesiologists in a clinical setting. This will give you firsthand insight into the daily responsibilities and challenges of the profession.
- Gain Research Experience: Engage in research projects related to anesthesiology or pain management. Research experience can enhance your medical school application and provide valuable insights into the field.
- Develop Clinical Skills: Seek out clinical rotations or volunteer positions that allow you to gain hands-on experience in healthcare settings. This will help you develop practical skills and a better understanding of patient care.
- Stay Updated with Medical Literature: Stay informed about the latest advancements and research in anesthesiology by reading medical journals and attending conferences or seminars.
- Build a Strong Support Network: Surround yourself with mentors, peers, and support systems who can provide guidance and encouragement throughout your educational journey.
Choosing the Right Medical School for Anesthesiology
When selecting a medical school, consider the following factors to ensure a strong foundation for your anesthesiology career:
- Accreditation: Choose an accredited medical school recognized by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME) or the American Osteopathic Association (AOA).
- Curriculum: Look for a medical school with a comprehensive curriculum that covers the core areas of anesthesiology, including pharmacology, critical care, and pain management.
- Clinical Rotations: Consider schools that offer diverse clinical rotation opportunities, allowing you to gain experience in various healthcare settings and specialties.
- Faculty and Research Opportunities: Choose a medical school with a strong faculty and research programs in anesthesiology. This can provide valuable mentorship and opportunities for involvement in cutting-edge research.
- Alumni Network: Consider the strength of the alumni network, as it can provide valuable connections and mentorship opportunities throughout your career.
The Residency Application Process

The residency application process for anesthesiology can be competitive, so it’s essential to start preparing early. Here are some key steps to enhance your chances of success:
- Step 1 Exam: The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 exam is a crucial component of your application. Aim for a competitive score to increase your chances of matching with a residency program.
- Letters of Recommendation: Seek letters of recommendation from faculty members and clinicians who can attest to your skills, work ethic, and potential as an anesthesiologist.
- Personal Statement: Craft a compelling personal statement that highlights your passion for anesthesiology, your unique experiences, and your commitment to patient care.
- Interview Preparation: Practice your interview skills and be prepared to discuss your clinical experiences, research interests, and career goals.
- Research Experience: Consider pursuing research opportunities during medical school to demonstrate your dedication and interest in the field.
Life as an Anesthesiologist

As an anesthesiologist, your daily life will be filled with a variety of responsibilities and challenges. Here’s a glimpse into the typical day-to-day:
- Preoperative Assessments: Meeting with patients before surgery to review their medical history, conduct physical examinations, and discuss anesthesia plans.
- Anesthesia Administration: Safely administering anesthesia medications, ensuring patient comfort and stability during surgical procedures.
- Postoperative Care: Monitoring patients in the recovery room, managing pain, and providing necessary follow-up care.
- Emergency Response: Being prepared to respond to medical emergencies, both in the operating room and in critical care settings.
- Continuing Education: Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in anesthesiology through conferences, workshops, and journal readings.
Challenges and Rewards of a Career in Anesthesiology

A career in anesthesiology comes with its unique set of challenges and rewards:
Challenges:
- High-stress environments and time constraints during surgical procedures.
- Managing patient anxiety and ensuring their comfort.
- Dealing with unexpected medical emergencies.
- Keeping up with rapidly evolving medical technologies and advancements.
Rewards:
- The satisfaction of providing essential care and ensuring patient safety.
- Building strong relationships with patients and their families.
- Constant learning and the opportunity to stay at the forefront of medical advancements.
- The potential for specialization and a diverse range of career paths.
Conclusion
Becoming an anesthesiologist is a challenging yet rewarding journey. It requires a strong foundation in medical knowledge, exceptional clinical skills, and a dedication to patient care. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can navigate the educational pathway and embark on a successful career in anesthesiology. Remember, with hard work, perseverance, and a passion for helping others, you can make a significant impact in the field of medicine as an anesthesiologist.
FAQ
What is the average salary for an anesthesiologist?
+
The average salary for anesthesiologists can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and specialty. However, anesthesiologists are known to be among the highest-paid medical specialties, with an average annual salary ranging from 300,000 to 450,000.
How long does it take to become an anesthesiologist?
+
The entire process of becoming an anesthesiologist typically takes around 12 to 14 years. This includes completing a 4-year undergraduate degree, a 4-year medical school program, and a 4-year residency in anesthesiology. Additionally, board certification and ongoing continuing medical education are required to maintain your license.
What are the key skills needed to succeed in anesthesiology?

+
Successful anesthesiologists possess a combination of medical knowledge, attention to detail, critical thinking abilities, excellent communication skills, and empathy. They must be able to make quick decisions, handle high-stress situations, and provide compassionate care to patients.
Are there any fellowship opportunities in anesthesiology?

+
Yes, fellowship programs are available for anesthesiologists who wish to further specialize in a specific area. Fellowships typically last one to two years and provide advanced training and research opportunities in fields such as pain medicine, critical care, pediatric anesthesiology, or neuroanesthesiology.
Can I pursue a career in anesthesiology if I didn’t major in a science-related field during my undergraduate studies?

+
While a science-related undergraduate major is not strictly required, it is highly recommended. Completing prerequisite courses in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics is essential for medical school admission. However, if you didn’t major in a science field, you may need to take additional courses to meet the requirements.