Persian Vs Arabic Language

Exploring the Distinctive Features of Persian and Arabic Languages
When it comes to languages, Persian and Arabic are two intriguing and diverse linguistic systems that have captivated scholars and language enthusiasts alike. With a rich history and cultural significance, these languages offer a unique perspective on communication and expression. In this blog post, we delve into the fascinating world of Persian and Arabic, uncovering their distinct characteristics, similarities, and the factors that set them apart.
The Historical and Cultural Background

To understand the essence of Persian and Arabic languages, it is essential to explore their historical and cultural foundations. Both languages have deep roots in ancient civilizations and have evolved over centuries, shaping the identities of their respective regions.
Persian Language

Persian, also known as Farsi, traces its origins back to ancient Persia, which encompassed modern-day Iran and parts of Central Asia. It is an Indo-European language that belongs to the Iranian branch of languages. Persian has a long and illustrious literary tradition, with renowned poets such as Rumi and Hafez contributing to its rich cultural heritage.
Arabic Language

Arabic, on the other hand, is a Semitic language that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. It is widely spoken across the Middle East and North Africa, making it one of the most geographically dispersed languages in the world. Arabic has played a significant role in the spread of Islam and has greatly influenced other languages in the region.
The Writing Systems

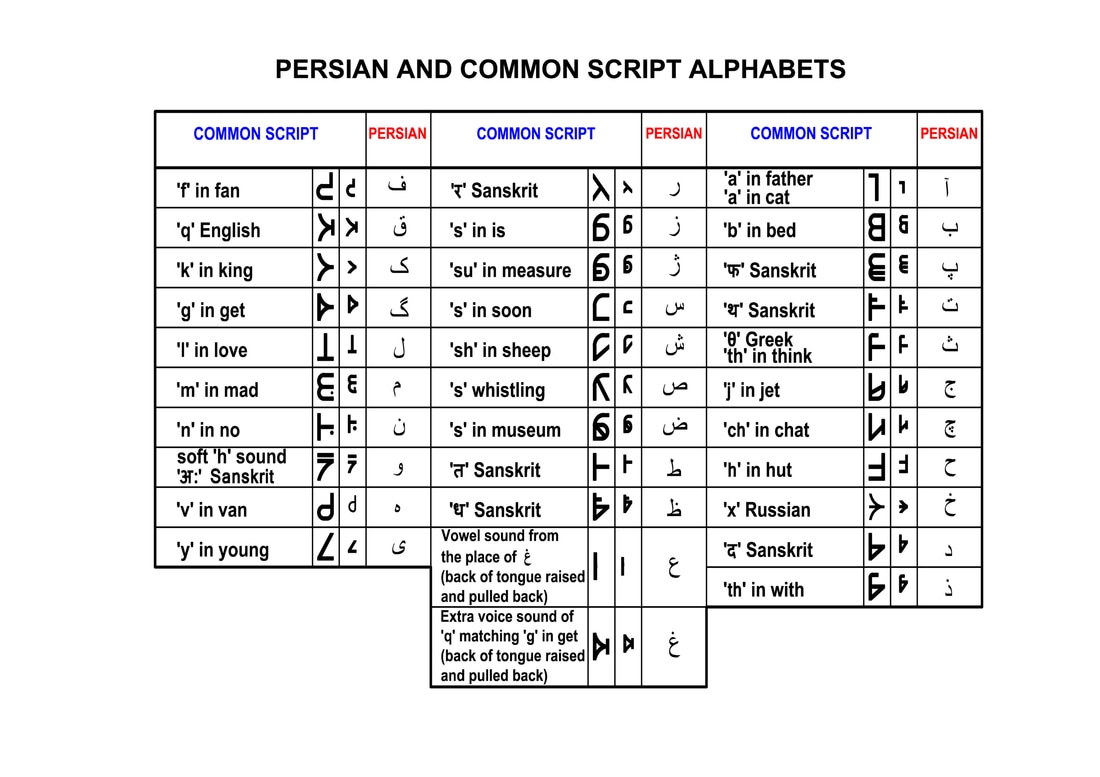
One of the most noticeable differences between Persian and Arabic lies in their writing systems. While both languages utilize the Arabic script, they have distinct variations and characteristics.
Persian Script

Persian uses a modified version of the Arabic script, known as the Perso-Arabic script. This script has evolved over time to accommodate the unique sounds and phonetics of the Persian language. One notable feature is the use of additional letters and diacritical marks to represent Persian sounds not found in Arabic.
Arabic Script

Arabic, on the other hand, adheres more closely to the traditional Arabic script. It consists of 28 letters, which are connected and written from right to left. Arabic script is known for its intricate and artistic calligraphic styles, making it an essential part of Islamic art and culture.
Phonetics and Pronunciation

Persian and Arabic languages exhibit distinct phonetic features that contribute to their unique sounds and accents.
Persian Phonetics

Persian has a relatively simple phonetic system compared to Arabic. It possesses a smaller set of consonants and vowels, making it easier for learners to grasp the pronunciation. Persian is known for its soft and melodic sound, with a focus on vowel harmony and stress patterns.
Arabic Phonetics

Arabic, in contrast, boasts a complex phonetic system with a wide range of consonant and vowel sounds. It includes unique phonemes, such as the pharyngeal fricatives and the emphatic consonants, which can be challenging for non-native speakers to produce accurately. Arabic pronunciation often requires precise tongue and lip movements, making it a captivating yet demanding language to master.
Grammar and Syntax

The grammatical structures of Persian and Arabic languages showcase both similarities and differences.
Persian Grammar

Persian grammar follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) word order, similar to other Indo-European languages. It has a relatively straightforward verb conjugation system, with verbs changing based on tense, aspect, and mood. Persian also employs a rich array of suffixes and prefixes to indicate case, number, and possession.
Arabic Grammar

Arabic grammar, on the other hand, is known for its intricate and flexible nature. It follows a subject-verb-object (SVO) word order, which is common among Semitic languages. Arabic verbs have a complex conjugation system, with various forms indicating person, gender, number, and mood. Additionally, Arabic grammar incorporates a unique system of case endings and noun declensions.
Vocabulary and Loanwords

Both Persian and Arabic languages have absorbed and influenced each other's vocabulary over time.
Persian Vocabulary

Persian has a vast vocabulary, influenced by its rich literary tradition and historical interactions with other languages. It has borrowed words from Arabic, Turkish, and even European languages, creating a diverse and colorful lexicon. Persian vocabulary often reflects its cultural and historical context, with words related to poetry, philosophy, and ancient traditions.
Arabic Vocabulary

Arabic, being the language of the Quran, has had a profound impact on the vocabulary of other languages in the region. It has lent numerous words to Persian, as well as to other languages like Urdu and Turkish. Arabic vocabulary encompasses a wide range of fields, including religion, science, and literature, making it a vital source of knowledge and cultural exchange.
Literary Traditions
Persian and Arabic languages have fostered rich literary traditions that have left an indelible mark on world literature.
Persian Literature
Persian literature boasts a long and illustrious history, with renowned poets and writers contributing to its development. From the epic poems of Ferdowsi to the mystical writings of Rumi, Persian literature has captivated readers with its depth and beauty. Persian poetry, in particular, is renowned for its use of symbolism, metaphor, and intricate rhyme schemes.
Arabic Literature
Arabic literature, similarly, has a rich and diverse tradition. It encompasses a wide range of genres, including poetry, prose, and religious texts. Arabic poetry, known for its rhythmic and musical qualities, has influenced literature across the globe. The Quran, considered the pinnacle of Arabic literature, has had a profound impact on the language and culture of the Islamic world.
Language Learning and Accessibility

For those interested in learning Persian or Arabic, it is essential to consider the availability of learning resources and the accessibility of the languages.
Learning Persian
Persian, being a widely spoken language with a growing global presence, has an increasing number of learning resources available. Online courses, language apps, and textbooks offer comprehensive guidance for learners at various levels. Additionally, the influence of Persian culture and its growing popularity in media and entertainment make it an attractive language to study.
Learning Arabic
Arabic, with its vast geographical reach, presents a diverse range of dialects and variations. Learning Arabic often involves focusing on a specific dialect, such as Modern Standard Arabic or a regional variant. While resources for learning Arabic are abundant, the complexity of the language and the variety of dialects can make it a challenging endeavor for beginners.
Conclusion

In exploring the distinctive features of Persian and Arabic languages, we uncover a world of linguistic diversity and cultural richness. From their historical roots to their unique writing systems, phonetics, grammar, and literary traditions, these languages offer a fascinating journey for language enthusiasts and scholars alike. Whether it is the melodic sounds of Persian or the intricate complexity of Arabic, both languages continue to captivate and inspire learners and researchers, fostering a deeper understanding of the world's linguistic tapestry.
What are the key differences between Persian and Arabic scripts?
+Persian uses a modified Arabic script with additional letters and diacritical marks to represent Persian sounds. Arabic script, on the other hand, remains closer to the traditional Arabic script, with 28 connected letters written from right to left.
How do Persian and Arabic grammar differ?
+Persian follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) word order, while Arabic follows a subject-verb-object (SVO) order. Persian has a simpler verb conjugation system, while Arabic verbs have a more complex conjugation with various forms indicating person, gender, and mood.
What is the influence of Arabic vocabulary on other languages?
+Arabic has lent numerous words to Persian, Urdu, Turkish, and other languages in the region. Its influence is particularly evident in fields such as religion, science, and literature, as Arabic vocabulary is often associated with knowledge and cultural exchange.
Which language is easier to learn, Persian or Arabic?
+Both languages have their own challenges and rewards. Persian may be easier for learners due to its simpler phonetic system and verb conjugation. However, Arabic’s influence and the variety of dialects can make it a fascinating yet complex language to master.
What are some recommended resources for learning Persian or Arabic?
+For Persian, online courses like Duolingo and textbooks such as “Persian: An Intermediate Textbook” by Shahrokh M. Keshavarz are highly recommended. As for Arabic, resources like the “Al-Kitaab” series and online platforms like Memrise offer comprehensive learning materials.


