Pictures Of Atrophic Vulvovaginitis

Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a condition that affects the female reproductive system, specifically the vulva and vagina. It is characterized by thinning and inflammation of the vaginal tissues, leading to various symptoms and discomfort. In this blog post, we will explore the topic of atrophic vulvovaginitis, its causes, symptoms, and the importance of seeking medical advice for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Atrophic Vulvovaginitis

Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a common condition that occurs when the levels of estrogen, a hormone essential for maintaining vaginal health, decrease. This can happen naturally during menopause, when the body's production of estrogen declines. However, it can also be triggered by other factors, such as certain medical conditions, medications, or surgical procedures.
The reduced estrogen levels result in changes to the vaginal tissues, causing them to become thinner, drier, and more fragile. This can lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a woman's quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors

The primary cause of atrophic vulvovaginitis is the decrease in estrogen levels. Here are some key factors that can contribute to the development of this condition:
- Menopause: Menopause is the most common trigger for atrophic vulvovaginitis. As women transition into menopause, their estrogen levels naturally decline, leading to vaginal atrophy.
- Hysterectomy: Surgical removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) can disrupt the normal estrogen production and distribution, increasing the risk of atrophic vulvovaginitis.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can disrupt hormone levels, potentially leading to atrophic vulvovaginitis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives or hormone therapy, can affect estrogen levels and contribute to the development of this condition.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: These cancer treatments can cause temporary or permanent changes in hormone levels, impacting vaginal health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

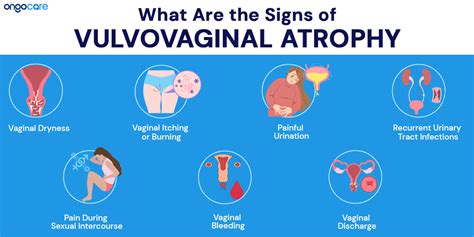
Atrophic vulvovaginitis can present with a variety of symptoms, which may include:
- Vaginal Dryness: The most common symptom is a persistent feeling of dryness in the vagina, which can make sexual intercourse painful or uncomfortable.
- Itching and Irritation: The thinning vaginal tissues can become itchy and irritated, leading to discomfort and potential skin irritation.
- Burning Sensation: Some women experience a burning sensation in the vaginal area, especially during urination or sexual activity.
- Light Bleeding: In severe cases, atrophic vulvovaginitis can cause light bleeding or spotting after sexual intercourse or pelvic exams.
- Pain and Discomfort: The vaginal tissues may become more sensitive, leading to pain during sexual activity or even during daily activities.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor will likely perform a pelvic exam and may recommend additional tests, such as hormone level assessments, to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Treatment Options
The treatment for atrophic vulvovaginitis aims to alleviate symptoms and improve vaginal health. Here are some common treatment approaches:
Hormone Therapy

Hormone therapy, such as estrogen replacement therapy, can help restore estrogen levels and improve vaginal tissue health. This can be administered through various methods, including:
- Vaginal Estrogen Creams or Ointments: These are applied directly to the vaginal area to provide localized estrogen treatment.
- Vaginal Estrogen Tablets or Rings: Inserted into the vagina, these devices release a steady dose of estrogen over time.
- Systemic Hormone Therapy: In some cases, oral or transdermal estrogen therapy may be recommended to address overall hormone balance.
Vaginal Moisturizers and Lubricants

Using vaginal moisturizers and lubricants can help alleviate vaginal dryness and make sexual intercourse more comfortable. These products can be applied regularly to maintain vaginal hydration.
Lifestyle Modifications

Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage atrophic vulvovaginitis. These include:
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help maintain overall vaginal hydration.
- Avoiding Irritants: Steer clear of scented soaps, douches, or other products that may irritate the vaginal area.
- Practicing Good Hygiene: Maintaining proper vaginal hygiene can help prevent infections and promote healing.
When to Seek Medical Advice

If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Atrophic vulvovaginitis can significantly impact your quality of life, and early diagnosis and treatment can provide much-needed relief.
Additionally, if you have any concerns or questions about your vaginal health, especially if you are going through menopause or have recently undergone a surgical procedure, seeking medical advice is crucial. Your doctor can provide personalized recommendations and ensure you receive the appropriate care.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is atrophic vulvovaginitis a serious condition?

+
While atrophic vulvovaginitis can cause discomfort and impact quality of life, it is generally not a life-threatening condition. However, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms effectively.
Can atrophic vulvovaginitis be prevented?

+
Preventing atrophic vulvovaginitis is not always possible, especially when it is a natural consequence of menopause. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good vaginal hygiene, and managing underlying medical conditions can help reduce the risk.
Are there any natural remedies for atrophic vulvovaginitis?

+
While some natural remedies, such as herbal supplements or vaginal suppositories, are available, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before trying them. They can guide you on the safety and effectiveness of these remedies for your specific case.
How long does it take for treatment to show results?

+
The response to treatment can vary depending on the individual and the chosen approach. Some women may experience relief within a few weeks, while others may require a longer duration of treatment. Consistency and adherence to the recommended treatment plan are crucial for optimal results.
Can atrophic vulvovaginitis recur after treatment?

+
Atrophic vulvovaginitis can recur, especially if the underlying cause is not addressed or managed effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, continuing with recommended treatments, and regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider can help prevent recurrence.
Conclusion

Atrophic vulvovaginitis is a common condition that can significantly impact a woman's well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By seeking timely medical advice and following recommended treatments, women can find relief and improve their quality of life. Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for addressing any concerns or questions you may have about atrophic vulvovaginitis.
💊 Note: This blog post provides general information about atrophic vulvovaginitis. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.


